Working with the Prana Vayus:
This is the eleventh entry in a series of twelve posts summarizing the basic material covered in the year long training which began in January of 2104 and will come to a completion on February 15th. Previous posts can be found on this blog page. A lot has been covered over the past year. If any questions arise, please feel free to contact me.
We are now working with the subtle energies, so some quietness and reflection is needed, even in dynamic postures. Meditation is primary in all poses, and the heart is the place to start. We are cultivating subtle streams of perception in both the fluid body and the etheric or spatial body, so some patience and persistence is required. Developing the skill of resting in stillness will allow the more subtle energies to reveal themselves.
Vayu means air or wind and the term Prana vayus refers to the five fundamental organizing movements of the energetic body. We will be working from the tensegrity/fluid body/pressure cavities perspective to make these movements both tangible and integrated. For anyone living in their body with sensitivity and intelligence, three major pressure cavities can be experienced, the cranial vault, the thoracic region, and the abdominal/pelvic region. Relative to the outside world, the head and abdominal cavities have positive or higher pressure and the thoracic cavity has a lower pressure. To present this in a more dramatic way, if you puncture the head or belly, stuff squirts out, but if you puncture the chest, it collapses inward, as in a collapsed lung. The basic point here is that this pressure gradient of the body is constantly moving energy toward the heart, i.e., pressure draws energy from higher to lower to create an internal equilibrium that is a major player in all of the fluid movements of the body.
This equilibrium can cover a whole spectrum from very dynamic, vital and healthy, to highly restricted and pathological. Our process in yoga physiology is to maximize the dynamic relationships for optimum health. And, it also turns out that in doing so we cultivate a deep inner presence in the heart center that is a place of infinite stillness and wholeness. Tada drashtuh svarupe avasthanam. We have to make it stable, of course, through practice and surrender, abhyasa and vairagyam.
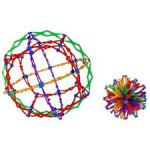
 We’ll begin with our Hoberman spheres and begin to feel the energies of the two directions: opening the sphere, expanding out from a center, which we can call the yang or centrifugal energy; and closing the sphere, condensing from the perimeter into the center, the yin or centripetal energy. When they are in balance, we can find a dynamically stable state of the sphere at any where along the spectrum from open to closed.
We’ll begin with our Hoberman spheres and begin to feel the energies of the two directions: opening the sphere, expanding out from a center, which we can call the yang or centrifugal energy; and closing the sphere, condensing from the perimeter into the center, the yin or centripetal energy. When they are in balance, we can find a dynamically stable state of the sphere at any where along the spectrum from open to closed.
When we come to the body and the Prana vayus, we first come the first, also known as the prana vayu, which governs the process of taking energies into the body/mind. (I’ll use a capital P when refering to the general term including all five, and a small p when referring to the intake. The prana vayu ,or prana, is an expanding field that creates space and invites energy to move into the body. This expansion is centered in the mid chest at the heart and balances the negative pressure usually felt in the chest which causes the outer world to press in upon the chest. If you hadn’t noticed, as people reach middle age and older, the chest has more often than not sunk in a bit from this pressure. Gravity and the aging belly energy also play a part in this sinking. By consciously finding, feeling, creating an expanding field from the heart, the chest opens, the heart lifts, and we are ready to be present to whatever the world offers us in the moment. If your connective tissues have fallen into a collapse of any level, it may take a while to reconfigure them. The intercostals and other chest muscles, as well as the diaphragm and mediastinum are involved. The prana vayu is usually associated with respiration, but on a sublte level governs everything you take in, from emotions to ideas, sensations and images.
As we are open systems, we have to balance taking in with moving out. The second vayu, apana, governs elimination, or what we let go of, at all levels. Apana is a squeezing or condensing energy, complimenting the expanding of the prana vayu. Expand to take in, squeeze to move out. Very simple. Most commentators focus on the downward flow, as solid and liquid wastes are eliminated predominantly out through the pelvic floor, but the apana is more complex than that. Sweating takes place throughout the body. Exhalation of the breath takes place through the nostrils or mouth. Regurgitation, a hopefully infrequent form of expelling unwanted material, moves out the mouth.
Ultimately apana is a radiallly condensing energy. However, it also has an unusual role in that the downwards aspect is also what governs the action of the legs and tail, real or imaginary. So we might say the the abdominal/pelvic cavity also can be expanded to include legs and tail. As we saw with the prana vayu, aging often takes a toll on the connective tissue structures of the body. The apana is a squeezing energy, but the belly has a positive or outgoing pressure. Aging often leads to this positive pressure creating the pot or beer belly, giving many middle agers the look of being slightly pregnant. With this state, the ‘sqeeziness’ is also much weaker, creating all sorts of problems from poor elimination and digestion, to lower back problems. From the perspective of Ayurveda, the medical wisdom of the Vedic tradition, poor elimination is the beginning of the disease process.
The samana vayu, classically associated with digestion, governs absorption. It is the decider or mediator between what comes in and what goes out. When healthy, we retain the ‘good stuff’ and eliminate the ‘bad stuff’. From the perspective of the pressure cavities, samana sits between the expanding center of prana in the chest and the squeezing center of apana in the pelvis. When healthy, the expanding nature of the abdomen is carefully 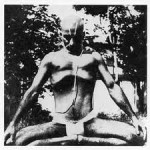 directed away from the abdominal wall and aligned with the spinal axis. Some of the energy lifts up through the diaphragm and into the heart, supporting the prana vayu; some of it extends downward to grow legs and tail, supporting the apana vayu. This action can be felt as a natural, mild uddiyana bandha. Here Krishnamacharya is demonstrating a slightly stronger version as part of pranayama practice.
directed away from the abdominal wall and aligned with the spinal axis. Some of the energy lifts up through the diaphragm and into the heart, supporting the prana vayu; some of it extends downward to grow legs and tail, supporting the apana vayu. This action can be felt as a natural, mild uddiyana bandha. Here Krishnamacharya is demonstrating a slightly stronger version as part of pranayama practice.
The vyana vayu circulates the energies throughout the body. First felt as the fluid flow of the blood, vyana also governs the nerve currents circulating information throughout the body and the flow of Prana through the subtle energy channels known as nadis.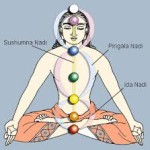 There are fourteen principal nadis, of which three are most commonly known. Ida is the lunar or cooling nadi associated with the feminine and parasympathetic nervous systems. Pingala, the solar or masculine nadi, works with the sympathetic nervous system. Susumna, the center channel, works with the central nervous system. There are some parallels with the meridian system in Chinese medicine.
There are fourteen principal nadis, of which three are most commonly known. Ida is the lunar or cooling nadi associated with the feminine and parasympathetic nervous systems. Pingala, the solar or masculine nadi, works with the sympathetic nervous system. Susumna, the center channel, works with the central nervous system. There are some parallels with the meridian system in Chinese medicine.
The vyana vayu has both expanding and condensing energies and also governs movement. The grace and elegance of the limbs in movement is an indication of healthy vyana.
The udana vayu is a fascinating one. An upward moving energy, udana governs growth and development at all levels of reality. At conception it facilitates embryological development and triggers the urge in the baby to move out of the womb and into the world by extending out through the crown chakra. This same energy takes the soul out of the body through the crown chakra at death. During your life, udana is a sustaining field of intelligence that integrates the other four pranas in an on-going urge to grow physically, emotionally and spiritually. When udana gets stuck, it feels as if our whole life is ‘stuck’. Coming back to the heart center and resting there is always a way to get ‘unstuck’.
In any poses you choose, find these energies. In dynamic postures such as standing poses and back bends, to much muscular energy is a sign of blockage in all the vayus. Start with opening the prana vayu and follow it through the others. In more restorative of meditative poses, find the udana vayu as a field of integration and stillness, where the whole body mind is awake and relaxed simultaneously.